节点不足以分配所有分片副本
编辑节点不足以分配所有分片副本
编辑将数据的副本(索引分片副本)分布在不同的节点上可以并行处理请求,从而加快搜索查询速度。这可以通过将副本分片的数量增加到最大值(节点总数减一)来实现,这也有助于防止硬件故障。如果索引具有首选层,Elasticsearch 将只在目标层中的节点上放置该索引的数据副本。
如果遇到“节点不足以分配所有分片副本”的警告,可以通过向集群(或正在使用层的情况下为层)添加更多节点,或者减少index.number_of_replicas索引设置来影响此行为。
要解决此问题,请按照以下步骤操作
分配副本分片的一种方法是添加可用区。这将增加 Elasticsearch 集群中的数据节点数量,以便可以分配副本分片。这可以通过编辑您的部署来完成。但首先,您需要发现索引的目标分配层。使用 Kibana 完成此操作。
使用 Kibana
- 登录Elastic Cloud 控制台。
-
在Elasticsearch 服务面板上,单击您的部署名称。
如果您的部署名称被禁用,您的 Kibana 实例可能不健康,在这种情况下,请联系Elastic 支持。如果您的部署不包含 Kibana,您只需要先启用它。
-
打开部署的侧边导航菜单(位于左上角的 Elastic 徽标下方),然后转到开发工具 > 控制台。
要检查索引的目标分配层,请使用获取索引设置 API 来检索index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference设置的配置值。
resp = client.indices.get_settings(
index="my-index-000001",
name="index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference",
flat_settings=True,
)
print(resp)
response = client.indices.get_settings( index: 'my-index-000001', name: 'index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference', flat_settings: true ) puts response
const response = await client.indices.getSettings({
index: "my-index-000001",
name: "index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference",
flat_settings: "true",
});
console.log(response);
GET /my-index-000001/_settings/index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference?flat_settings
响应将如下所示
{
"my-index-000001": {
"settings": {
"index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference": "data_warm,data_hot"
}
}
}
|
表示允许在此索引上分配的逗号分隔的数据层节点角色列表,列表中的第一个角色具有更高的优先级,即索引的目标层。例如,在此示例中,层首选项是 |
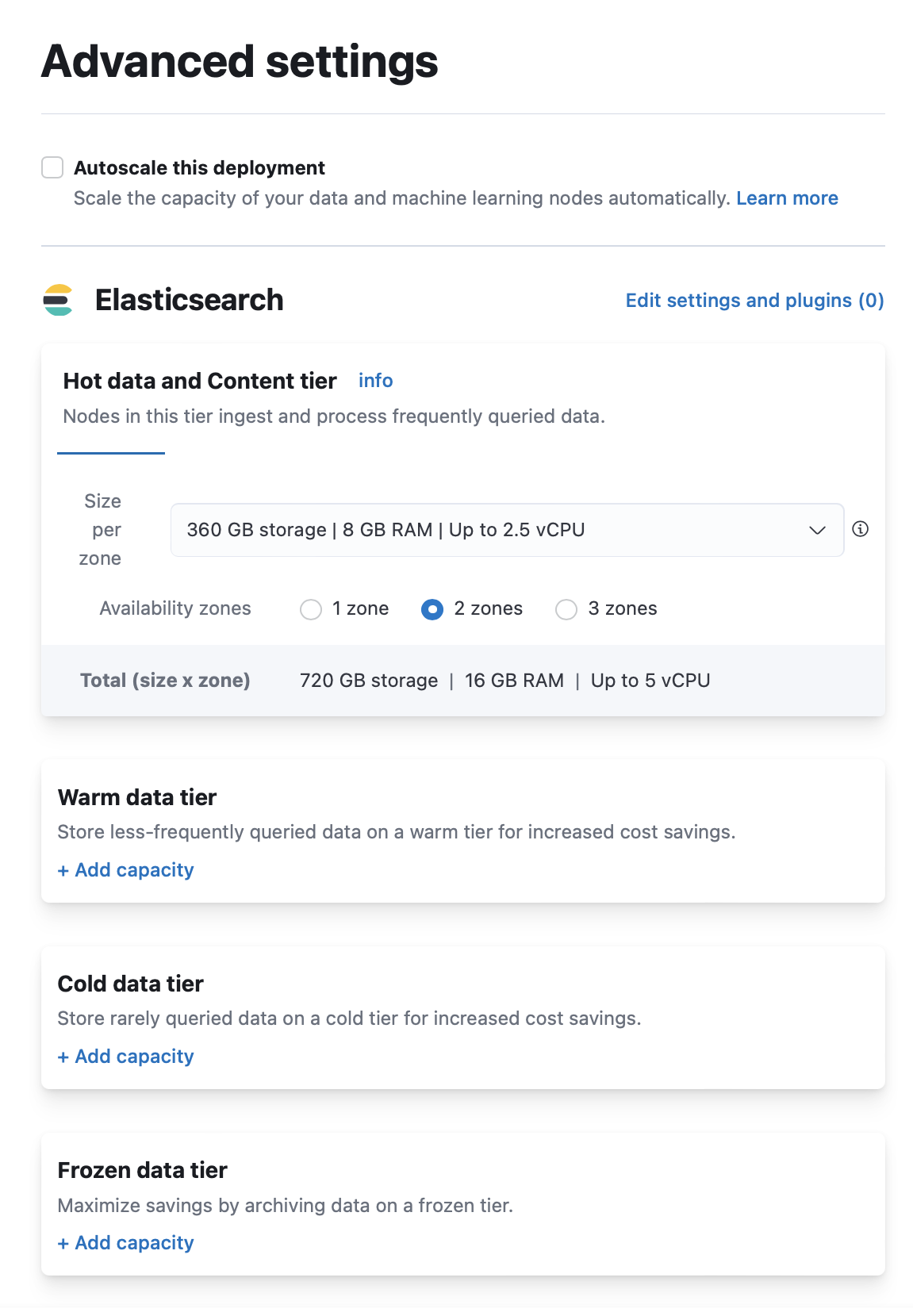
现在您知道了层,您需要增加该层中的节点数量,以便可以分配副本。为此,您可以增加每个区域的大小以增加您已经在使用的可用区中的节点数量,或者增加可用区的数量。通过单击屏幕左上角的三个水平条并选择管理此部署返回到部署的登录页面。在此页面上,单击管理按钮,然后选择编辑部署。请注意,您必须登录到https://cloud.elastic.co/才能执行此操作。在 Elasticsearch 部分,找到无法分配副本分片的层。
-
选项 1:增加每个区域的大小
- 查看每个区域的大小下拉菜单中的值。您在此处选择的每 64 GB RAM,每个区域都会创建一个节点。如果您当前选择的 RAM 小于或等于 64 GB,则每个区域都有一个节点。如果您选择 128 GB RAM,则每个区域将获得 2 个节点。如果您选择 192 GB RAM,则每个区域将获得 3 个节点,依此类推。如果该值小于最大可能值,您可以为该层选择更高的值以添加更多节点。
-
选项 2:增加可用区的数量
- 找到可用区选择。如果少于 3 个,您可以为该层选择更多数量的可用区。
如果无法增加每个区域的大小或可用区的数量,您可以减少索引数据的副本数。我们将通过检查index.number_of_replicas索引设置并减小配置的值来实现此目的。
- 如上所述访问 Kibana。
-
检查
index.number_of_replicas索引设置。resp = client.indices.get_settings( index="my-index-000001", name="index.number_of_replicas", ) print(resp)response = client.indices.get_settings( index: 'my-index-000001', name: 'index.number_of_replicas' ) puts response
const response = await client.indices.getSettings({ index: "my-index-000001", name: "index.number_of_replicas", }); console.log(response);GET /my-index-000001/_settings/index.number_of_replicas
响应将如下所示
-
使用
_cat/nodesAPI 查找目标层中的节点数量。resp = client.cat.nodes( h="node.role", ) print(resp)response = client.cat.nodes( h: 'node.role' ) puts response
const response = await client.cat.nodes({ h: "node.role", }); console.log(response);GET /_cat/nodes?h=node.role
响应将如下所示,每行包含一个节点。
himrst mv himrst
您可以计算包含表示目标层的字母的行数,以了解您有多少个节点。有关详细信息,请参阅查询参数。上面的示例包含两行
h,因此热层中有两个节点。 -
减少此索引所需的副本分片的总数。由于副本分片不能与主分片位于同一节点上(高可用性),因此新值需要小于或等于上面找到的节点数减一。由于上面的示例在热层中找到 2 个节点,因此
index.number_of_replicas的最大值为 1。resp = client.indices.put_settings( index="my-index-000001", settings={ "index": { "number_of_replicas": 1 } }, ) print(resp)response = client.indices.put_settings( index: 'my-index-000001', body: { index: { number_of_replicas: 1 } } ) puts responseconst response = await client.indices.putSettings({ index: "my-index-000001", settings: { index: { number_of_replicas: 1, }, }, }); console.log(response);index.number_of_replicas索引配置的新值从之前的2减少到1。它可以低至 0,但是对于可搜索快照索引以外的索引将其配置为 0 可能会导致节点重启期间出现临时可用性损失,或者在数据损坏的情况下导致永久性数据丢失。
为了分配副本分片,您可以向 Elasticsearch 集群添加更多节点,并将索引的目标层节点角色分配给新节点。
要检查索引的目标分配层,请使用获取索引设置 API 来检索index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference设置的配置值。
resp = client.indices.get_settings(
index="my-index-000001",
name="index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference",
flat_settings=True,
)
print(resp)
response = client.indices.get_settings( index: 'my-index-000001', name: 'index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference', flat_settings: true ) puts response
const response = await client.indices.getSettings({
index: "my-index-000001",
name: "index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference",
flat_settings: "true",
});
console.log(response);
GET /my-index-000001/_settings/index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference?flat_settings
响应将如下所示
{
"my-index-000001": {
"settings": {
"index.routing.allocation.include._tier_preference": "data_warm,data_hot"
}
}
}
|
表示允许在此索引上分配的逗号分隔的数据层节点角色列表,列表中的第一个角色具有更高的优先级,即索引的目标层。例如,在此示例中,层首选项是 |
或者,如果不需要向 Elasticsearch 集群添加更多节点,请检查index.number_of_replicas索引设置并减小配置的值。
-
检查具有未分配副本分片的索引的
index.number_of_replicas索引设置。resp = client.indices.get_settings( index="my-index-000001", name="index.number_of_replicas", ) print(resp)response = client.indices.get_settings( index: 'my-index-000001', name: 'index.number_of_replicas' ) puts response
const response = await client.indices.getSettings({ index: "my-index-000001", name: "index.number_of_replicas", }); console.log(response);GET /my-index-000001/_settings/index.number_of_replicas
响应将如下所示
-
使用
_cat/nodesAPI 查找目标层中的节点数量。resp = client.cat.nodes( h="node.role", ) print(resp)response = client.cat.nodes( h: 'node.role' ) puts response
const response = await client.cat.nodes({ h: "node.role", }); console.log(response);GET /_cat/nodes?h=node.role
响应将如下所示,每行包含一个节点。
himrst mv himrst
您可以计算包含表示目标层的字母的行数,以了解您有多少个节点。有关详细信息,请参阅查询参数。上面的示例包含两行
h,因此热层中有两个节点。 -
减少此索引所需的副本分片的总数。由于副本分片不能与主分片位于同一节点上(高可用性),因此新值需要小于或等于上面找到的节点数减一。由于上面的示例在热层中找到 2 个节点,因此
index.number_of_replicas的最大值为 1。resp = client.indices.put_settings( index="my-index-000001", settings={ "index": { "number_of_replicas": 1 } }, ) print(resp)response = client.indices.put_settings( index: 'my-index-000001', body: { index: { number_of_replicas: 1 } } ) puts responseconst response = await client.indices.putSettings({ index: "my-index-000001", settings: { index: { number_of_replicas: 1, }, }, }); console.log(response);index.number_of_replicas索引配置的新值从之前的2减少到1。它可以低至 0,但是对于可搜索快照索引以外的索引将其配置为 0 可能会导致节点重启期间出现临时可用性损失,或者在数据损坏的情况下导致永久性数据丢失。