百分位数聚合
编辑百分位数聚合
编辑一个多值指标聚合,用于计算从聚合文档中提取的数值的一个或多个百分位数。这些值可以从文档中的特定数值字段或直方图字段中提取。
百分位数显示观察到的值达到某个百分比的点。例如,第 95 个百分位数是大于 95% 观察值的数值。
百分位数常用于查找异常值。在正态分布中,第 0.13 个和第 99.87 个百分位数代表平均值的三个标准差。任何超出三个标准差的数据通常被认为是异常值。
当检索一系列百分位数时,它们可以用来估计数据分布并确定数据是否倾斜、双峰等。
假设您的数据包含网站加载时间。平均加载时间和中位数加载时间对于管理员来说并没有太大的用处。最大值可能很有趣,但它很容易被单个缓慢的响应所扭曲。
让我们来看一下代表加载时间的一系列百分位数
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time"
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time'
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time",
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time"
}
}
}
}
默认情况下,percentile指标将生成一系列百分位数:[1, 5, 25, 50, 75, 95, 99]。响应将如下所示
{
...
"aggregations": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"values": {
"1.0": 10.0,
"5.0": 30.0,
"25.0": 170.0,
"50.0": 445.0,
"75.0": 720.0,
"95.0": 940.0,
"99.0": 980.0
}
}
}
}
如您所见,聚合将返回默认范围内每个百分位数的计算值。如果我们假设响应时间以毫秒为单位,那么很明显,网页通常在 10-720 毫秒内加载,但偶尔会飙升到 940-980 毫秒。
通常,管理员只对异常值(极端百分位数)感兴趣。我们可以只指定我们感兴趣的百分比(请求的百分位数必须是 0-100(含)之间的值)
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"percents": [
95,
99,
99.9
]
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time',
percents: [
95,
99,
99.9
]
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time",
percents: [95, 99, 99.9],
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"percents": [ 95, 99, 99.9 ]
}
}
}
}
键值响应
编辑默认情况下,keyed标志设置为true,它将唯一的字符串键与每个桶关联,并将范围作为哈希而不是数组返回。将keyed标志设置为false将禁用此行为
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"keyed": False
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time',
keyed: false
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time",
keyed: false,
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"keyed": false
}
}
}
}
响应
{
...
"aggregations": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"values": [
{
"key": 1.0,
"value": 10.0
},
{
"key": 5.0,
"value": 30.0
},
{
"key": 25.0,
"value": 170.0
},
{
"key": 50.0,
"value": 445.0
},
{
"key": 75.0,
"value": 720.0
},
{
"key": 95.0,
"value": 940.0
},
{
"key": 99.0,
"value": 980.0
}
]
}
}
}
脚本
编辑如果您需要对未索引的值运行聚合,请使用运行时字段。例如,如果我们的加载时间以毫秒为单位,但您希望以秒为单位计算百分位数
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
runtime_mappings={
"load_time.seconds": {
"type": "long",
"script": {
"source": "emit(doc['load_time'].value / params.timeUnit)",
"params": {
"timeUnit": 1000
}
}
}
},
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time.seconds"
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
runtime_mappings: {
'load_time.seconds' => {
type: 'long',
script: {
source: "emit(doc['load_time'].value / params.timeUnit)",
params: {
"timeUnit": 1000
}
}
}
},
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time.seconds'
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
runtime_mappings: {
"load_time.seconds": {
type: "long",
script: {
source: "emit(doc['load_time'].value / params.timeUnit)",
params: {
timeUnit: 1000,
},
},
},
},
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time.seconds",
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"runtime_mappings": {
"load_time.seconds": {
"type": "long",
"script": {
"source": "emit(doc['load_time'].value / params.timeUnit)",
"params": {
"timeUnit": 1000
}
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time.seconds"
}
}
}
}
百分位数是(通常)近似的
编辑有许多不同的算法可以计算百分位数。简单的实现只是将所有值存储在排序数组中。要查找第 50 个百分位数,只需找到位于my_array[count(my_array) * 0.5]的值。
显然,简单的实现无法扩展——排序数组的大小会随着数据集中的值的数量线性增长。为了在 Elasticsearch 集群中计算可能数十亿个值的百分位数,计算的是近似百分位数。
percentile指标使用的算法称为 TDigest(由 Ted Dunning 在使用 T-Digest 计算精确分位数中介绍)。
使用此指标时,需要注意以下几点准则
- 精度与
q(1-q)成正比。这意味着极端百分位数(例如 99%)比不太极端的百分位数(例如中位数)更准确 - 对于少量值,百分位数非常准确(如果数据足够小,则可能 100% 准确)。
- 随着桶中值的数量增加,算法开始近似百分位数。它有效地以牺牲精度来换取内存节省。不准确的精确程度很难概括,因为它取决于您的数据分布和被聚合的数据量
下图显示了均匀分布的相对误差,这取决于收集的值的数量和请求的百分位数
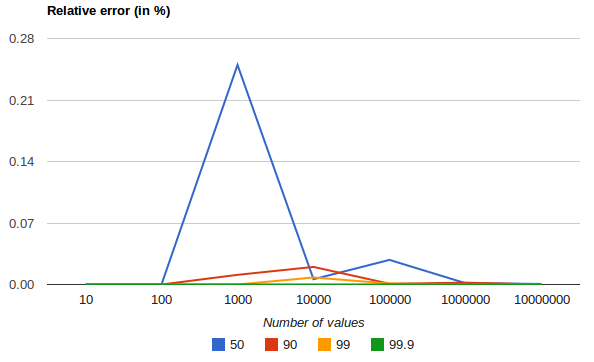
它显示了极端百分位数的精度如何更好。对于大量值,误差减小的原因是大数定律使值的分布越来越均匀,并且 t-digest 树可以更好地总结它。对于更倾斜的分布,情况并非如此。
百分位数聚合也是非确定性的。这意味着您可以使用相同的数据获得略微不同的结果。
压缩
编辑近似算法必须在内存利用率和估计精度之间取得平衡。可以使用compression参数来控制这种平衡
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"tdigest": {
"compression": 200
}
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time',
tdigest: {
compression: 200
}
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time",
tdigest: {
compression: 200,
},
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"tdigest": {
"compression": 200
}
}
}
}
}
TDigest 算法使用多个“节点”来近似百分位数——可用的节点越多,精度越高(并且内存占用越大),与数据量成正比。compression参数将节点的最大数量限制为20 * compression。
因此,通过增加压缩值,您可以提高百分位数的精度,但代价是需要更多内存。较大的压缩值还会使算法变慢,因为底层树状数据结构的大小会增加,从而导致更昂贵的操作。默认压缩值为100。
一个“节点”大约使用 32 字节的内存,因此在最坏的情况下(大量按顺序排序的数据到达),默认设置将生成一个大约 64KB 大小的 TDigest。在实践中,数据往往更随机,TDigest 将使用更少的内存。
执行提示
编辑TDigest 的默认实现针对性能进行了优化,可以扩展到数百万甚至数十亿个样本值,同时保持可接受的精度水平(在某些情况下,数百万个样本的相对误差接近 1%)。可以通过将参数execution_hint设置为值high_accuracy来使用针对精度优化的实现
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"tdigest": {
"execution_hint": "high_accuracy"
}
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time',
tdigest: {
execution_hint: 'high_accuracy'
}
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time",
tdigest: {
execution_hint: "high_accuracy",
},
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"tdigest": {
"execution_hint": "high_accuracy"
}
}
}
}
}
此选项可以提高精度(在某些情况下,数百万个样本的相对误差接近 0.01%),但是百分位数查询完成所需的时间会增加 2 倍到 10 倍。
HDR 直方图
编辑HDR Histogram(高动态范围直方图)是一种替代实现,在计算延迟测量的百分位数时非常有用,因为它可能比 t-digest 实现更快,但代价是内存占用更大。此实现保持固定的最坏情况百分比误差(指定为有效数字的数量)。这意味着,如果在设置为 3 位有效数字的直方图中记录从 1 微秒到 1 小时(3,600,000,000 微秒)的值的数据,它将为高达 1 毫秒的值保持 1 微秒的值分辨率,以及对于最大跟踪值(1 小时)保持 3.6 秒(或更好)的值分辨率。
可以通过在请求中指定hdr参数来使用 HDR Histogram
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"percents": [
95,
99,
99.9
],
"hdr": {
"number_of_significant_value_digits": 3
}
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: 'load_time',
percents: [
95,
99,
99.9
],
hdr: {
number_of_significant_value_digits: 3
}
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
load_time_outlier: {
percentiles: {
field: "load_time",
percents: [95, 99, 99.9],
hdr: {
number_of_significant_value_digits: 3,
},
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
GET latency/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"load_time_outlier": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "load_time",
"percents": [ 95, 99, 99.9 ],
"hdr": {
"number_of_significant_value_digits": 3
}
}
}
}
}
|
|
|
|
|
HDRHistogram 仅支持正值,如果传递负值,则会出错。如果值的范围未知,则最好不要使用 HDRHistogram,因为这可能会导致高内存使用率。
缺失值
编辑missing参数定义如何处理缺少值的文档。默认情况下,它们将被忽略,但也可以将它们视为具有值。
resp = client.search(
index="latency",
size=0,
aggs={
"grade_percentiles": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "grade",
"missing": 10
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
response = client.search(
index: 'latency',
body: {
size: 0,
aggregations: {
grade_percentiles: {
percentiles: {
field: 'grade',
missing: 10
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
const response = await client.search({
index: "latency",
size: 0,
aggs: {
grade_percentiles: {
percentiles: {
field: "grade",
missing: 10,
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);