ES|QL 查询入门
编辑ES|QL 查询入门
编辑本指南介绍如何使用 ES|QL 查询和聚合数据。
此入门指南也以 交互式 Python 笔记本 的形式在 elasticsearch-labs GitHub 仓库中提供。
前提条件
编辑要按照本指南中的查询操作进行操作,您可以设置自己的部署,或者使用 Elastic 的公共 ES|QL 演示环境。
首先导入一些示例数据。在 Kibana 中,打开主菜单并选择 开发工具。运行以下两个请求
resp = client.indices.create(
index="sample_data",
mappings={
"properties": {
"client_ip": {
"type": "ip"
},
"message": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
resp1 = client.bulk(
index="sample_data",
operations=[
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T12:15:03.360Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.2.162",
"message": "Connected to 10.1.0.3",
"event_duration": 3450233
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T12:27:28.948Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.2.113",
"message": "Connected to 10.1.0.2",
"event_duration": 2764889
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:33:34.937Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.0.5",
"message": "Disconnected",
"event_duration": 1232382
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:51:54.732Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.3.15",
"message": "Connection error",
"event_duration": 725448
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:52:55.015Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.3.15",
"message": "Connection error",
"event_duration": 8268153
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:53:55.832Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.3.15",
"message": "Connection error",
"event_duration": 5033755
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:55:01.543Z",
"client_ip": "172.21.3.15",
"message": "Connected to 10.1.0.1",
"event_duration": 1756467
}
],
)
print(resp1)
response = client.indices.create(
index: 'sample_data',
body: {
mappings: {
properties: {
client_ip: {
type: 'ip'
},
message: {
type: 'keyword'
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
response = client.bulk(
index: 'sample_data',
body: [
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T12:15:03.360Z',
client_ip: '172.21.2.162',
message: 'Connected to 10.1.0.3',
event_duration: 3_450_233
},
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T12:27:28.948Z',
client_ip: '172.21.2.113',
message: 'Connected to 10.1.0.2',
event_duration: 2_764_889
},
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T13:33:34.937Z',
client_ip: '172.21.0.5',
message: 'Disconnected',
event_duration: 1_232_382
},
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T13:51:54.732Z',
client_ip: '172.21.3.15',
message: 'Connection error',
event_duration: 725_448
},
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T13:52:55.015Z',
client_ip: '172.21.3.15',
message: 'Connection error',
event_duration: 8_268_153
},
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T13:53:55.832Z',
client_ip: '172.21.3.15',
message: 'Connection error',
event_duration: 5_033_755
},
{
index: {}
},
{
"@timestamp": '2023-10-23T13:55:01.543Z',
client_ip: '172.21.3.15',
message: 'Connected to 10.1.0.1',
event_duration: 1_756_467
}
]
)
puts response
const response = await client.indices.create({
index: "sample_data",
mappings: {
properties: {
client_ip: {
type: "ip",
},
message: {
type: "keyword",
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
const response1 = await client.bulk({
index: "sample_data",
operations: [
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T12:15:03.360Z",
client_ip: "172.21.2.162",
message: "Connected to 10.1.0.3",
event_duration: 3450233,
},
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T12:27:28.948Z",
client_ip: "172.21.2.113",
message: "Connected to 10.1.0.2",
event_duration: 2764889,
},
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:33:34.937Z",
client_ip: "172.21.0.5",
message: "Disconnected",
event_duration: 1232382,
},
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:51:54.732Z",
client_ip: "172.21.3.15",
message: "Connection error",
event_duration: 725448,
},
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:52:55.015Z",
client_ip: "172.21.3.15",
message: "Connection error",
event_duration: 8268153,
},
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:53:55.832Z",
client_ip: "172.21.3.15",
message: "Connection error",
event_duration: 5033755,
},
{
index: {},
},
{
"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:55:01.543Z",
client_ip: "172.21.3.15",
message: "Connected to 10.1.0.1",
event_duration: 1756467,
},
],
});
console.log(response1);
PUT sample_data
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"client_ip": {
"type": "ip"
},
"message": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
PUT sample_data/_bulk
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T12:15:03.360Z", "client_ip": "172.21.2.162", "message": "Connected to 10.1.0.3", "event_duration": 3450233}
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T12:27:28.948Z", "client_ip": "172.21.2.113", "message": "Connected to 10.1.0.2", "event_duration": 2764889}
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:33:34.937Z", "client_ip": "172.21.0.5", "message": "Disconnected", "event_duration": 1232382}
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:51:54.732Z", "client_ip": "172.21.3.15", "message": "Connection error", "event_duration": 725448}
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:52:55.015Z", "client_ip": "172.21.3.15", "message": "Connection error", "event_duration": 8268153}
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:53:55.832Z", "client_ip": "172.21.3.15", "message": "Connection error", "event_duration": 5033755}
{"index": {}}
{"@timestamp": "2023-10-23T13:55:01.543Z", "client_ip": "172.21.3.15", "message": "Connected to 10.1.0.1", "event_duration": 1756467}
本指南中使用的数据集已预加载到 Elastic ES|QL 公共演示环境中。访问 ela.st/ql 以开始使用它。
运行 ES|QL 查询
编辑在 Kibana 中,您可以使用控制台或发现来运行 ES|QL 查询
要开始在控制台中使用 ES|QL,请打开主菜单并选择 开发工具。
一个 ES|QL 查询 API 请求的通用结构如下
POST /_query?format=txt
{
"query": """
"""
}
在两组三个引号之间输入实际的 ES|QL 查询。例如
POST /_query?format=txt
{
"query": """
FROM sample_data
"""
}
要开始在发现中使用 ES|QL,请打开主菜单并选择 发现。接下来,从应用程序菜单栏中选择 尝试 ES|QL。
调整时间过滤器,使其包含示例数据中的时间戳(2023 年 10 月 23 日)。
切换到 ES|QL 模式后,查询栏会显示一个示例查询。您可以将此查询替换为本入门指南中的查询。
为了更方便地编写查询,自动完成功能会提供可能的命令和函数建议。
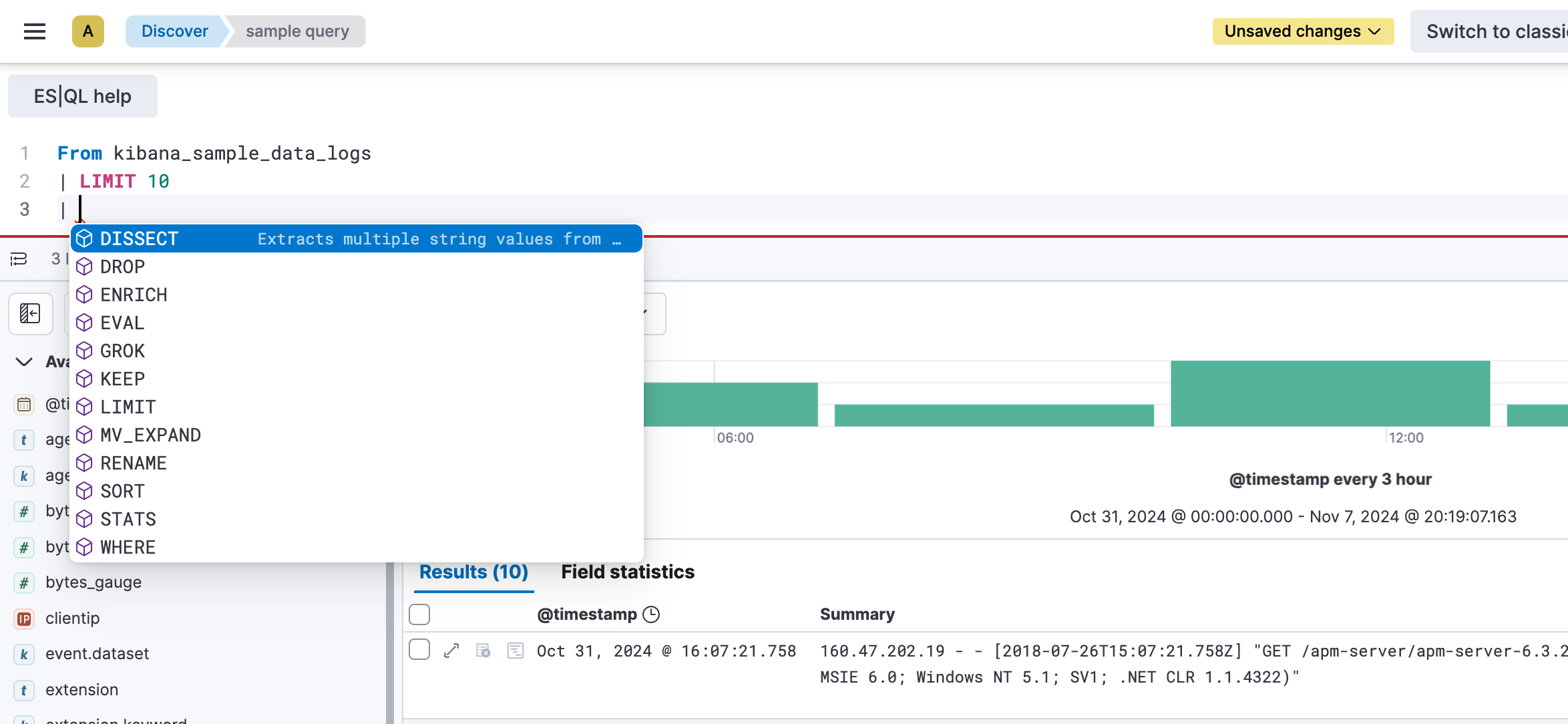
您可以通过拖动编辑器底部边框来调整其高度。
您的第一个 ES|QL 查询
编辑每个 ES|QL 查询都以 源命令 开头。源命令生成一个表,通常包含来自 Elasticsearch 的数据。
FROM 源命令返回一个包含来自数据流、索引或别名的文档的表。结果表中的每一行都代表一个文档。此查询从 sample_data 索引返回最多 1000 个文档
FROM sample_data
每一列对应一个字段,可以通过该字段的名称访问。
ES|QL 关键词不区分大小写。以下查询与前一个查询相同
from sample_data
处理命令
编辑源命令后面可以跟一个或多个 处理命令,并用管道字符分隔:|。处理命令通过添加、删除或更改行和列来更改输入表。处理命令可以执行过滤、投影、聚合等操作。
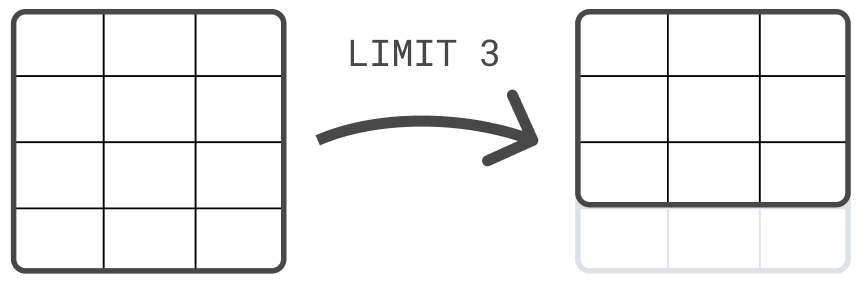
例如,您可以使用 LIMIT 命令限制返回的行数,最多 10,000 行
FROM sample_data | LIMIT 3
为了提高可读性,您可以将每个命令放在单独一行。但是,您不必这样做。以下查询与前一个查询相同
FROM sample_data | LIMIT 3
排序表
编辑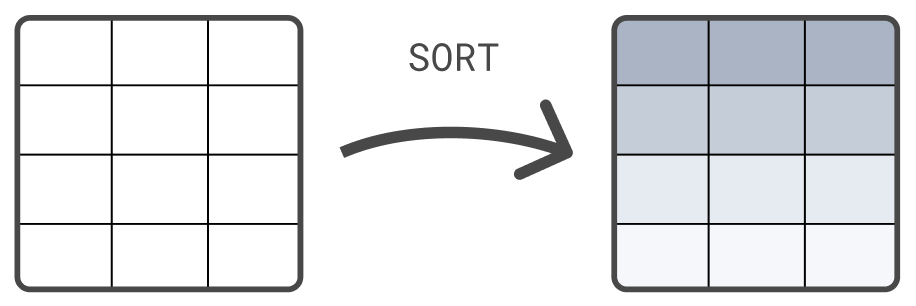
另一个处理命令是 SORT 命令。默认情况下,FROM 返回的行没有定义的排序顺序。使用 SORT 命令根据一个或多个列对行进行排序
FROM sample_data | SORT @timestamp DESC
查询数据
编辑使用 WHERE 命令查询数据。例如,查找持续时间超过 5 毫秒的所有事件
FROM sample_data | WHERE event_duration > 5000000
WHERE 支持多个 运算符。例如,您可以使用 LIKE 对 message 列运行通配符查询
FROM sample_data | WHERE message LIKE "Connected*"
更多处理命令
编辑还有许多其他处理命令,例如 KEEP 和 DROP 用于保留或删除列,ENRICH 用于使用 Elasticsearch 中的索引数据丰富表,以及 DISSECT 和 GROK 用于处理数据。有关所有处理命令的概述,请参阅 处理命令。
链接处理命令
编辑您可以链接处理命令,并用管道字符分隔:|。每个处理命令都作用于前一个命令的输出表。查询的结果是由最后一个处理命令生成的表。
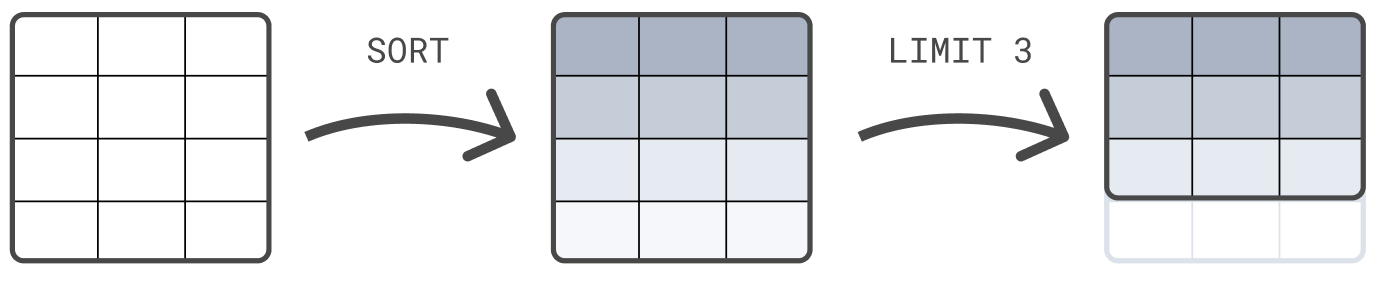
以下示例首先根据 @timestamp 对表进行排序,然后将结果集限制为 3 行
FROM sample_data | SORT @timestamp DESC | LIMIT 3
处理命令的顺序很重要。在对这 3 行排序之前,首先将结果集限制为 3 行,很可能会返回与本示例不同的结果,在本示例中,排序在限制之前。
计算值
编辑使用 EVAL 命令将列附加到表中,并使用计算值。例如,以下查询附加一个 duration_ms 列。该列中的值是通过将 event_duration 除以 1,000,000 计算得出的。换句话说:将 event_duration 从纳秒转换为毫秒。
FROM sample_data | EVAL duration_ms = event_duration/1000000.0
EVAL 支持多个 函数。例如,要将数字四舍五入到指定位数的最接近的数字,请使用 ROUND 函数
FROM sample_data | EVAL duration_ms = ROUND(event_duration/1000000.0, 1)
计算统计数据
编辑ES|QL 不仅可以用于查询数据,还可以用于聚合数据。使用 STATS ... BY 命令计算统计数据。例如,中位持续时间
FROM sample_data | STATS median_duration = MEDIAN(event_duration)
您可以使用一个命令计算多个统计数据
FROM sample_data | STATS median_duration = MEDIAN(event_duration), max_duration = MAX(event_duration)
使用 BY 根据一个或多个列对计算的统计数据进行分组。例如,计算每个客户端 IP 的中位持续时间
FROM sample_data | STATS median_duration = MEDIAN(event_duration) BY client_ip
访问列
编辑您可以通过列名访问列。如果名称包含特殊字符,则需要使用反引号 (`) 进行引用。
为 EVAL 或 STATS 创建的列分配显式名称是可选的。如果您不提供名称,则新列名将等于函数表达式。例如
FROM sample_data | EVAL event_duration/1000000.0
在此查询中,EVAL 添加了一个名为 event_duration/1000000.0 的新列。由于其名称包含特殊字符,因此要访问此列,请使用反引号将其引用
FROM sample_data | EVAL event_duration/1000000.0 | STATS MEDIAN(`event_duration/1000000.0`)
创建直方图
编辑为了跟踪随时间变化的统计数据,ES|QL 使您能够使用 BUCKET 函数创建直方图。BUCKET 创建用户友好的桶大小,并为每一行返回一个值,该值对应于该行所属的结果桶。
将 BUCKET 与 STATS ... BY 结合使用以创建直方图。例如,计算每小时的事件数
FROM sample_data | STATS c = COUNT(*) BY bucket = BUCKET(@timestamp, 24, "2023-10-23T00:00:00Z", "2023-10-23T23:59:59Z")
或每小时的中位持续时间
FROM sample_data | KEEP @timestamp, event_duration | STATS median_duration = MEDIAN(event_duration) BY bucket = BUCKET(@timestamp, 24, "2023-10-23T00:00:00Z", "2023-10-23T23:59:59Z")
丰富数据
编辑ES|QL 使您能够使用 丰富 表格,其中包含来自 Elasticsearch 中索引的数据,使用 ENRICH 命令。
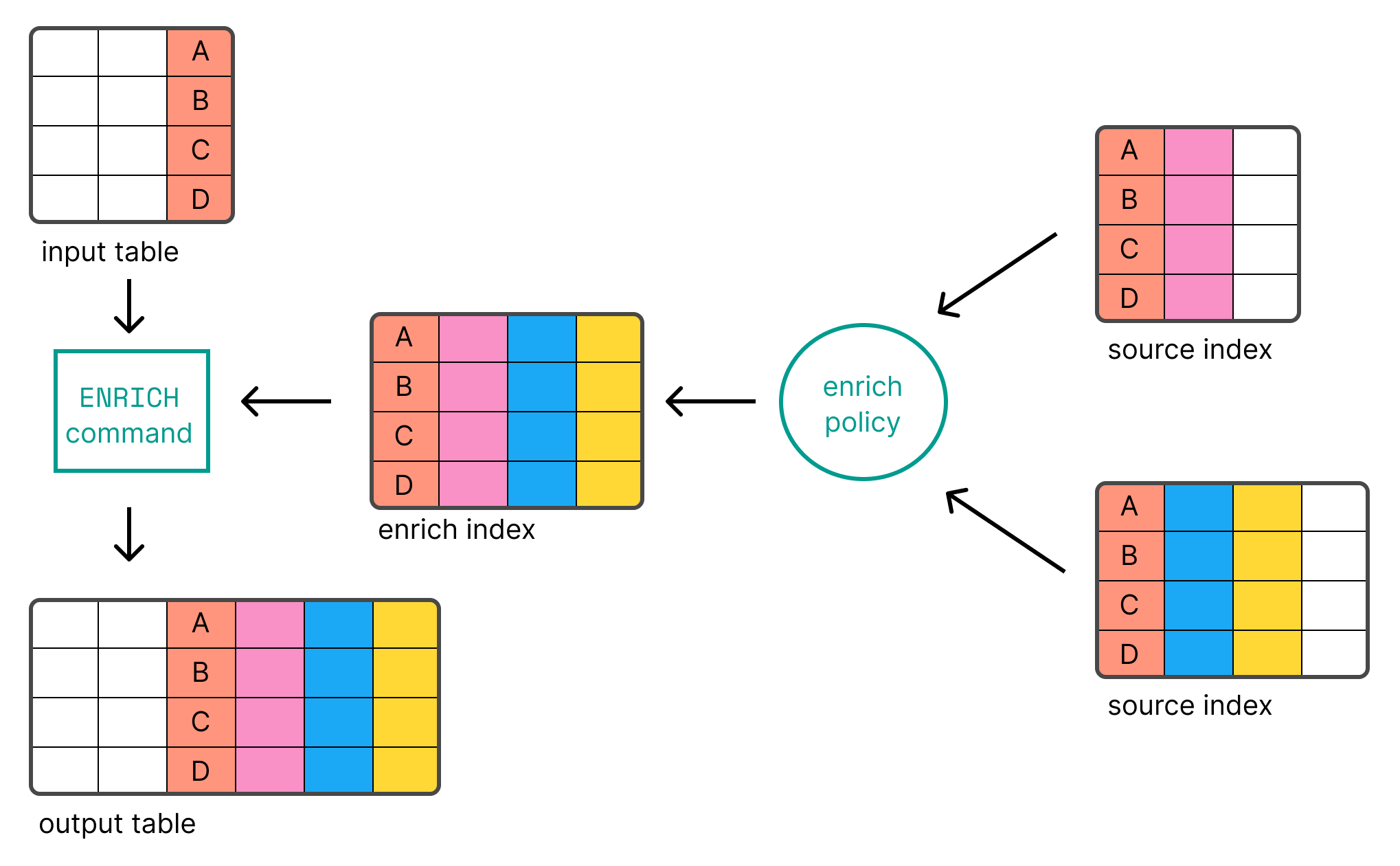
在您可以使用 ENRICH 之前,您首先需要 创建 并 执行 一个 丰富策略。
以下请求创建并执行一个名为 clientip_policy 的策略。该策略将 IP 地址链接到环境(“开发”、“QA”或“生产”)
resp = client.indices.create(
index="clientips",
mappings={
"properties": {
"client_ip": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"env": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
)
print(resp)
resp1 = client.bulk(
index="clientips",
operations=[
{
"index": {}
},
{
"client_ip": "172.21.0.5",
"env": "Development"
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"client_ip": "172.21.2.113",
"env": "QA"
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"client_ip": "172.21.2.162",
"env": "QA"
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"client_ip": "172.21.3.15",
"env": "Production"
},
{
"index": {}
},
{
"client_ip": "172.21.3.16",
"env": "Production"
}
],
)
print(resp1)
resp2 = client.enrich.put_policy(
name="clientip_policy",
match={
"indices": "clientips",
"match_field": "client_ip",
"enrich_fields": [
"env"
]
},
)
print(resp2)
resp3 = client.enrich.execute_policy(
name="clientip_policy",
wait_for_completion=False,
)
print(resp3)
response = client.indices.create(
index: 'clientips',
body: {
mappings: {
properties: {
client_ip: {
type: 'keyword'
},
env: {
type: 'keyword'
}
}
}
}
)
puts response
response = client.bulk(
index: 'clientips',
body: [
{
index: {}
},
{
client_ip: '172.21.0.5',
env: 'Development'
},
{
index: {}
},
{
client_ip: '172.21.2.113',
env: 'QA'
},
{
index: {}
},
{
client_ip: '172.21.2.162',
env: 'QA'
},
{
index: {}
},
{
client_ip: '172.21.3.15',
env: 'Production'
},
{
index: {}
},
{
client_ip: '172.21.3.16',
env: 'Production'
}
]
)
puts response
response = client.enrich.put_policy(
name: 'clientip_policy',
body: {
match: {
indices: 'clientips',
match_field: 'client_ip',
enrich_fields: [
'env'
]
}
}
)
puts response
response = client.enrich.execute_policy(
name: 'clientip_policy',
wait_for_completion: false
)
puts response
const response = await client.indices.create({
index: "clientips",
mappings: {
properties: {
client_ip: {
type: "keyword",
},
env: {
type: "keyword",
},
},
},
});
console.log(response);
const response1 = await client.bulk({
index: "clientips",
operations: [
{
index: {},
},
{
client_ip: "172.21.0.5",
env: "Development",
},
{
index: {},
},
{
client_ip: "172.21.2.113",
env: "QA",
},
{
index: {},
},
{
client_ip: "172.21.2.162",
env: "QA",
},
{
index: {},
},
{
client_ip: "172.21.3.15",
env: "Production",
},
{
index: {},
},
{
client_ip: "172.21.3.16",
env: "Production",
},
],
});
console.log(response1);
const response2 = await client.enrich.putPolicy({
name: "clientip_policy",
match: {
indices: "clientips",
match_field: "client_ip",
enrich_fields: ["env"],
},
});
console.log(response2);
const response3 = await client.enrich.executePolicy({
name: "clientip_policy",
wait_for_completion: "false",
});
console.log(response3);
PUT clientips
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"client_ip": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"env": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
PUT clientips/_bulk
{ "index" : {}}
{ "client_ip": "172.21.0.5", "env": "Development" }
{ "index" : {}}
{ "client_ip": "172.21.2.113", "env": "QA" }
{ "index" : {}}
{ "client_ip": "172.21.2.162", "env": "QA" }
{ "index" : {}}
{ "client_ip": "172.21.3.15", "env": "Production" }
{ "index" : {}}
{ "client_ip": "172.21.3.16", "env": "Production" }
PUT /_enrich/policy/clientip_policy
{
"match": {
"indices": "clientips",
"match_field": "client_ip",
"enrich_fields": ["env"]
}
}
PUT /_enrich/policy/clientip_policy/_execute?wait_for_completion=false
在 ela.st/ql 上的演示环境中,已经创建并执行了一个名为 clientip_policy 的丰富策略。该策略将 IP 地址链接到环境(“开发”、“QA”或“生产”)。
创建并执行策略后,您可以将其与 ENRICH 命令一起使用
FROM sample_data | KEEP @timestamp, client_ip, event_duration | EVAL client_ip = TO_STRING(client_ip) | ENRICH clientip_policy ON client_ip WITH env
您可以在后续命令中使用 ENRICH 命令添加的新 env 列。例如,计算每个环境的中位持续时间
FROM sample_data | KEEP @timestamp, client_ip, event_duration | EVAL client_ip = TO_STRING(client_ip) | ENRICH clientip_policy ON client_ip WITH env | STATS median_duration = MEDIAN(event_duration) BY env
有关使用 ES|QL 进行数据丰富的更多信息,请参阅 数据丰富。
处理数据
编辑您的数据可能包含您想要 构建 的非结构化字符串,以便更容易分析数据。例如,示例数据包含以下日志消息
"Connected to 10.1.0.3"
通过从这些消息中提取 IP 地址,您可以确定哪个 IP 接受了最多的客户端连接。
要在查询时构建非结构化字符串,您可以使用 ES|QL DISSECT 和 GROK 命令。DISSECT 通过使用基于分隔符的模式分解字符串来工作。GROK 的工作原理类似,但使用正则表达式。这使得 GROK 更加强大,但通常也更慢。
在本例中,不需要正则表达式,因为 message 很简单:“已连接到”,后跟服务器 IP。要匹配此字符串,您可以使用以下 DISSECT 命令
FROM sample_data
| DISSECT message "Connected to %{server_ip}"
这会将 server_ip 列添加到具有匹配此模式的 message 的那些行。对于其他行,server_ip 的值为 null。
您可以使用 DISSECT 命令添加的新 server_ip 列在后续命令中。例如,要确定每个服务器接受了多少连接
FROM sample_data
| WHERE STARTS_WITH(message, "Connected to")
| DISSECT message "Connected to %{server_ip}"
| STATS COUNT(*) BY server_ip
有关使用 ES|QL 处理数据的更多信息,请参阅 使用 DISSECT 和 GROK 处理数据。