- Elasticsearch 指南其他版本
- 8.17 中的新功能
- Elasticsearch 基础
- 快速入门
- 设置 Elasticsearch
- 升级 Elasticsearch
- 索引模块
- 映射
- 文本分析
- 索引模板
- 数据流
- 摄取管道
- 别名
- 搜索您的数据
- 重新排名
- 查询 DSL
- 聚合
- 地理空间分析
- 连接器
- EQL
- ES|QL
- SQL
- 脚本
- 数据管理
- 自动缩放
- 监视集群
- 汇总或转换数据
- 设置高可用性集群
- 快照和还原
- 保护 Elastic Stack 的安全
- Watcher
- 命令行工具
- elasticsearch-certgen
- elasticsearch-certutil
- elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token
- elasticsearch-croneval
- elasticsearch-keystore
- elasticsearch-node
- elasticsearch-reconfigure-node
- elasticsearch-reset-password
- elasticsearch-saml-metadata
- elasticsearch-service-tokens
- elasticsearch-setup-passwords
- elasticsearch-shard
- elasticsearch-syskeygen
- elasticsearch-users
- 优化
- 故障排除
- 修复常见的集群问题
- 诊断未分配的分片
- 向系统中添加丢失的层
- 允许 Elasticsearch 在系统中分配数据
- 允许 Elasticsearch 分配索引
- 索引将索引分配过滤器与数据层节点角色混合,以在数据层之间移动
- 没有足够的节点来分配所有分片副本
- 单个节点上索引的分片总数已超过
- 每个节点的分片总数已达到
- 故障排除损坏
- 修复磁盘空间不足的数据节点
- 修复磁盘空间不足的主节点
- 修复磁盘空间不足的其他角色节点
- 启动索引生命周期管理
- 启动快照生命周期管理
- 从快照恢复
- 故障排除损坏的存储库
- 解决重复的快照策略失败问题
- 故障排除不稳定的集群
- 故障排除发现
- 故障排除监控
- 故障排除转换
- 故障排除 Watcher
- 故障排除搜索
- 故障排除分片容量健康问题
- 故障排除不平衡的集群
- 捕获诊断信息
- REST API
- API 约定
- 通用选项
- REST API 兼容性
- 自动缩放 API
- 行为分析 API
- 紧凑和对齐文本 (CAT) API
- 集群 API
- 跨集群复制 API
- 连接器 API
- 数据流 API
- 文档 API
- 丰富 API
- EQL API
- ES|QL API
- 功能 API
- Fleet API
- 图表探索 API
- 索引 API
- 别名是否存在
- 别名
- 分析
- 分析索引磁盘使用量
- 清除缓存
- 克隆索引
- 关闭索引
- 创建索引
- 创建或更新别名
- 创建或更新组件模板
- 创建或更新索引模板
- 创建或更新索引模板(旧版)
- 删除组件模板
- 删除悬挂索引
- 删除别名
- 删除索引
- 删除索引模板
- 删除索引模板(旧版)
- 存在
- 字段使用情况统计信息
- 刷新
- 强制合并
- 获取别名
- 获取组件模板
- 获取字段映射
- 获取索引
- 获取索引设置
- 获取索引模板
- 获取索引模板(旧版)
- 获取映射
- 导入悬挂索引
- 索引恢复
- 索引段
- 索引分片存储
- 索引统计信息
- 索引模板是否存在(旧版)
- 列出悬挂索引
- 打开索引
- 刷新
- 解析索引
- 解析集群
- 翻转
- 收缩索引
- 模拟索引
- 模拟模板
- 拆分索引
- 解冻索引
- 更新索引设置
- 更新映射
- 索引生命周期管理 API
- 推理 API
- 信息 API
- 摄取 API
- 许可 API
- Logstash API
- 机器学习 API
- 机器学习异常检测 API
- 机器学习数据帧分析 API
- 机器学习训练模型 API
- 迁移 API
- 节点生命周期 API
- 查询规则 API
- 重新加载搜索分析器 API
- 存储库计量 API
- 汇总 API
- 根 API
- 脚本 API
- 搜索 API
- 搜索应用程序 API
- 可搜索快照 API
- 安全 API
- 身份验证
- 更改密码
- 清除缓存
- 清除角色缓存
- 清除权限缓存
- 清除 API 密钥缓存
- 清除服务帐户令牌缓存
- 创建 API 密钥
- 创建或更新应用程序权限
- 创建或更新角色映射
- 创建或更新角色
- 批量创建或更新角色 API
- 批量删除角色 API
- 创建或更新用户
- 创建服务帐户令牌
- 委托 PKI 身份验证
- 删除应用程序权限
- 删除角色映射
- 删除角色
- 删除服务帐户令牌
- 删除用户
- 禁用用户
- 启用用户
- 注册 Kibana
- 注册节点
- 获取 API 密钥信息
- 获取应用程序权限
- 获取内置权限
- 获取角色映射
- 获取角色
- 查询角色
- 获取服务帐户
- 获取服务帐户凭据
- 获取安全设置
- 获取令牌
- 获取用户权限
- 获取用户
- 授予 API 密钥
- 具有权限
- 使 API 密钥失效
- 使令牌失效
- OpenID Connect 准备身份验证
- OpenID Connect 身份验证
- OpenID Connect 注销
- 查询 API 密钥信息
- 查询用户
- 更新 API 密钥
- 更新安全设置
- 批量更新 API 密钥
- SAML 准备身份验证
- SAML 身份验证
- SAML 注销
- SAML 失效
- SAML 完成注销
- SAML 服务提供商元数据
- SSL 证书
- 激活用户配置文件
- 禁用用户配置文件
- 启用用户配置文件
- 获取用户配置文件
- 建议用户配置文件
- 更新用户配置文件数据
- 具有用户配置文件权限
- 创建跨集群 API 密钥
- 更新跨集群 API 密钥
- 快照和还原 API
- 快照生命周期管理 API
- SQL API
- 同义词 API
- 文本结构 API
- 转换 API
- 使用情况 API
- Watcher API
- 定义
- 迁移指南
- 发行说明
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.17.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.16.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.16.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.15.5
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.15.4
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.15.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.15.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.15.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.15.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.14.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.14.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.14.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.14.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.13.4
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.13.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.13.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.13.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.13.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.12.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.12.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.12.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.11.4
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.11.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.11.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.11.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.11.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.10.4
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.10.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.10.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.10.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.10.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.9.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.9.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.9.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.8.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.8.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.8.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.7.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.7.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.6.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.6.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.6.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.5.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.5.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.5.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.5.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.4.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.4.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.4.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.4.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.3.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.3.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.3.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.3.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.2.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.2.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.2.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.2.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.1.3
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.1.2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.1.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.1.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.0
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.0-rc2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.0-rc1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.0-beta1
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.0-alpha2
- Elasticsearch 版本 8.0.0-alpha1
- 依赖项和版本
数据摄取管道
编辑数据摄取管道
编辑数据摄取管道允许您在索引之前对数据执行常见的转换。例如,您可以使用管道来删除字段、从文本中提取值以及丰富您的数据。
管道由一系列可配置的任务组成,称为处理器。每个处理器按顺序运行,对传入的文档进行特定的更改。在处理器运行后,Elasticsearch 会将转换后的文档添加到您的数据流或索引中。
您可以使用 Kibana 的数据摄取管道功能或数据摄取 API来创建和管理数据摄取管道。Elasticsearch 将管道存储在集群状态中。
先决条件
编辑创建和管理管道
编辑在 Kibana 中,打开主菜单并单击Stack Management > 数据摄取管道。从列表视图中,您可以
- 查看您的管道列表并深入了解详细信息
- 编辑或克隆现有管道
- 删除管道
要创建管道,请单击创建管道 > 新管道。有关示例教程,请参阅示例:解析日志。
从 CSV 创建新管道选项允许您使用 CSV 创建一个数据摄取管道,将自定义数据映射到Elastic Common Schema (ECS)。将自定义数据映射到 ECS 使数据更易于搜索,并允许您重用其他数据集中的可视化。要开始使用,请查看将自定义数据映射到 ECS。
您还可以使用数据摄取 API来创建和管理管道。以下创建管道 API请求创建一个包含两个set处理器,然后是一个lowercase处理器的管道。处理器按照指定的顺序依次运行。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", description="My optional pipeline description", processors=[ { "set": { "description": "My optional processor description", "field": "my-long-field", "value": 10 } }, { "set": { "description": "Set 'my-boolean-field' to true", "field": "my-boolean-field", "value": True } }, { "lowercase": { "field": "my-keyword-field" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { description: 'My optional pipeline description', processors: [ { set: { description: 'My optional processor description', field: 'my-long-field', value: 10 } }, { set: { description: "Set 'my-boolean-field' to true", field: 'my-boolean-field', value: true } }, { lowercase: { field: 'my-keyword-field' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", description: "My optional pipeline description", processors: [ { set: { description: "My optional processor description", field: "my-long-field", value: 10, }, }, { set: { description: "Set 'my-boolean-field' to true", field: "my-boolean-field", value: true, }, }, { lowercase: { field: "my-keyword-field", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "description": "My optional pipeline description", "processors": [ { "set": { "description": "My optional processor description", "field": "my-long-field", "value": 10 } }, { "set": { "description": "Set 'my-boolean-field' to true", "field": "my-boolean-field", "value": true } }, { "lowercase": { "field": "my-keyword-field" } } ] }
管理管道版本
编辑当您创建或更新管道时,您可以指定一个可选的version整数。您可以将此版本号与if_version参数结合使用,以有条件地更新管道。当指定if_version参数时,成功的更新会递增管道的版本。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline-id { "version": 1, "processors": [ ... ] }
要使用 API 取消设置version号,请替换或更新管道而不指定version参数。
测试管道
编辑在生产环境中使用管道之前,我们建议您使用示例文档对其进行测试。在 Kibana 中创建或编辑管道时,单击添加文档。在文档选项卡中,提供示例文档并单击运行管道。
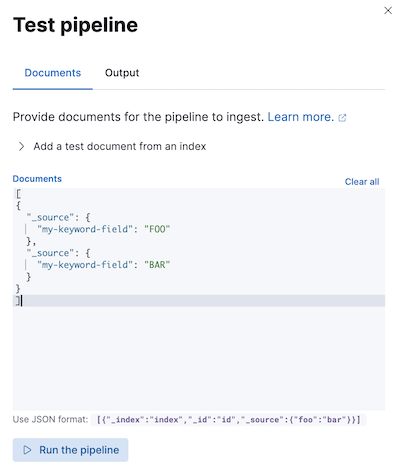
您还可以使用模拟管道 API来测试管道。您可以在请求路径中指定已配置的管道。例如,以下请求测试my-pipeline。
resp = client.ingest.simulate( id="my-pipeline", docs=[ { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "FOO" } }, { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "BAR" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.simulate( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { docs: [ { _source: { "my-keyword-field": 'FOO' } }, { _source: { "my-keyword-field": 'BAR' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.simulate({ id: "my-pipeline", docs: [ { _source: { "my-keyword-field": "FOO", }, }, { _source: { "my-keyword-field": "BAR", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
POST _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline/_simulate { "docs": [ { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "FOO" } }, { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "BAR" } } ] }
或者,您可以在请求正文中指定管道及其处理器。
resp = client.ingest.simulate( pipeline={ "processors": [ { "lowercase": { "field": "my-keyword-field" } } ] }, docs=[ { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "FOO" } }, { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "BAR" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.simulate( body: { pipeline: { processors: [ { lowercase: { field: 'my-keyword-field' } } ] }, docs: [ { _source: { "my-keyword-field": 'FOO' } }, { _source: { "my-keyword-field": 'BAR' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.simulate({ pipeline: { processors: [ { lowercase: { field: "my-keyword-field", }, }, ], }, docs: [ { _source: { "my-keyword-field": "FOO", }, }, { _source: { "my-keyword-field": "BAR", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
POST _ingest/pipeline/_simulate { "pipeline": { "processors": [ { "lowercase": { "field": "my-keyword-field" } } ] }, "docs": [ { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "FOO" } }, { "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "BAR" } } ] }
API 返回转换后的文档
{ "docs": [ { "doc": { "_index": "_index", "_id": "_id", "_version": "-3", "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "foo" }, "_ingest": { "timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:03.000Z" } } }, { "doc": { "_index": "_index", "_id": "_id", "_version": "-3", "_source": { "my-keyword-field": "bar" }, "_ingest": { "timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:04.000Z" } } } ] }
将管道添加到索引请求
编辑使用pipeline查询参数将管道应用于单个或批量索引请求中的文档。
resp = client.index( index="my-data-stream", pipeline="my-pipeline", document={ "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:05.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "foo" }, ) print(resp) resp1 = client.bulk( index="my-data-stream", pipeline="my-pipeline", operations=[ { "create": {} }, { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:06.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "foo" }, { "create": {} }, { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:07.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "bar" } ], ) print(resp1)
response = client.index( index: 'my-data-stream', pipeline: 'my-pipeline', body: { "@timestamp": '2099-03-07T11:04:05.000Z', "my-keyword-field": 'foo' } ) puts response response = client.bulk( index: 'my-data-stream', pipeline: 'my-pipeline', body: [ { create: {} }, { "@timestamp": '2099-03-07T11:04:06.000Z', "my-keyword-field": 'foo' }, { create: {} }, { "@timestamp": '2099-03-07T11:04:07.000Z', "my-keyword-field": 'bar' } ] ) puts response
const response = await client.index({ index: "my-data-stream", pipeline: "my-pipeline", document: { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:05.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "foo", }, }); console.log(response); const response1 = await client.bulk({ index: "my-data-stream", pipeline: "my-pipeline", operations: [ { create: {}, }, { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:06.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "foo", }, { create: {}, }, { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:07.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "bar", }, ], }); console.log(response1);
POST my-data-stream/_doc?pipeline=my-pipeline { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:05.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "foo" } PUT my-data-stream/_bulk?pipeline=my-pipeline { "create":{ } } { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:06.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "foo" } { "create":{ } } { "@timestamp": "2099-03-07T11:04:07.000Z", "my-keyword-field": "bar" }
您还可以将pipeline参数与按查询更新或重新索引API 一起使用。
resp = client.update_by_query( index="my-data-stream", pipeline="my-pipeline", ) print(resp) resp1 = client.reindex( source={ "index": "my-data-stream" }, dest={ "index": "my-new-data-stream", "op_type": "create", "pipeline": "my-pipeline" }, ) print(resp1)
response = client.update_by_query( index: 'my-data-stream', pipeline: 'my-pipeline' ) puts response response = client.reindex( body: { source: { index: 'my-data-stream' }, dest: { index: 'my-new-data-stream', op_type: 'create', pipeline: 'my-pipeline' } } ) puts response
const response = await client.updateByQuery({ index: "my-data-stream", pipeline: "my-pipeline", }); console.log(response); const response1 = await client.reindex({ source: { index: "my-data-stream", }, dest: { index: "my-new-data-stream", op_type: "create", pipeline: "my-pipeline", }, }); console.log(response1);
POST my-data-stream/_update_by_query?pipeline=my-pipeline POST _reindex { "source": { "index": "my-data-stream" }, "dest": { "index": "my-new-data-stream", "op_type": "create", "pipeline": "my-pipeline" } }
设置默认管道
编辑使用index.default_pipeline索引设置来设置默认管道。如果未指定pipeline参数,Elasticsearch 会将此管道应用于索引请求。
设置最终管道
编辑使用index.final_pipeline索引设置来设置最终管道。即使未指定请求或默认管道,Elasticsearch 也会在它们之后应用此管道。
Beats 的管道
编辑要将数据摄取管道添加到 Elastic Beat,请在<BEAT_NAME>.yml中的output.elasticsearch下指定pipeline参数。例如,对于 Filebeat,您将在filebeat.yml中指定pipeline。
output.elasticsearch: hosts: ["localhost:9200"] pipeline: my-pipeline
Fleet 和 Elastic Agent 的管道
编辑Elastic Agent 集成附带默认的数据摄取管道,用于在索引之前预处理和丰富数据。Fleet使用包含管道索引设置的索引模板应用这些管道。Elasticsearch 根据数据流的命名方案将这些模板与您的 Fleet 数据流进行匹配。
每个默认集成管道都会调用一个不存在的、未版本的*@custom数据摄取管道。如果未更改,此管道调用对您的数据没有影响。但是,您可以修改此调用来为跨升级保留的集成创建自定义管道。请参阅教程:使用自定义数据摄取管道转换数据以了解更多信息。
Fleet 没有为自定义日志集成提供默认的数据摄取管道,但您可以使用索引模板或自定义配置为该集成指定管道。
-
创建并测试您的数据摄取管道。将您的管道命名为
logs-<数据集名称>-default。这使得跟踪集成的管道更加容易。例如,以下请求为
my-app数据集创建一个管道。管道的名称为logs-my_app-default。PUT _ingest/pipeline/logs-my_app-default { "description": "Pipeline for `my_app` dataset", "processors": [ ... ] }
-
创建一个索引模板,其中包含
index.default_pipeline或index.final_pipeline索引设置中的管道。确保该模板启用了数据流。模板的索引模式应与logs-<数据集名称>-*匹配。您可以使用 Kibana 的索引管理功能或创建索引模板 API来创建此模板。
例如,以下请求创建与
logs-my_app-*匹配的模板。该模板使用一个组件模板,其中包含index.default_pipeline索引设置。resp = client.cluster.put_component_template( name="logs-my_app-settings", template={ "settings": { "index.default_pipeline": "logs-my_app-default", "index.lifecycle.name": "logs" } }, ) print(resp) resp1 = client.indices.put_index_template( name="logs-my_app-template", index_patterns=[ "logs-my_app-*" ], data_stream={}, priority=500, composed_of=[ "logs-my_app-settings", "logs-my_app-mappings" ], ) print(resp1)
const response = await client.cluster.putComponentTemplate({ name: "logs-my_app-settings", template: { settings: { "index.default_pipeline": "logs-my_app-default", "index.lifecycle.name": "logs", }, }, }); console.log(response); const response1 = await client.indices.putIndexTemplate({ name: "logs-my_app-template", index_patterns: ["logs-my_app-*"], data_stream: {}, priority: 500, composed_of: ["logs-my_app-settings", "logs-my_app-mappings"], }); console.log(response1);
# Creates a component template for index settings PUT _component_template/logs-my_app-settings { "template": { "settings": { "index.default_pipeline": "logs-my_app-default", "index.lifecycle.name": "logs" } } } # Creates an index template matching `logs-my_app-*` PUT _index_template/logs-my_app-template { "index_patterns": ["logs-my_app-*"], "data_stream": { }, "priority": 500, "composed_of": ["logs-my_app-settings", "logs-my_app-mappings"] }
- 在 Fleet 中添加或编辑自定义日志集成时,单击配置集成 > 自定义日志文件 > 高级选项。
-
在数据集名称中,指定您数据集的名称。Fleet 将为该集成将新数据添加到生成的
logs-<数据集名称>-default数据流中。例如,如果您数据集的名称为
my_app,则 Fleet 会将新数据添加到logs-my_app-default数据流中。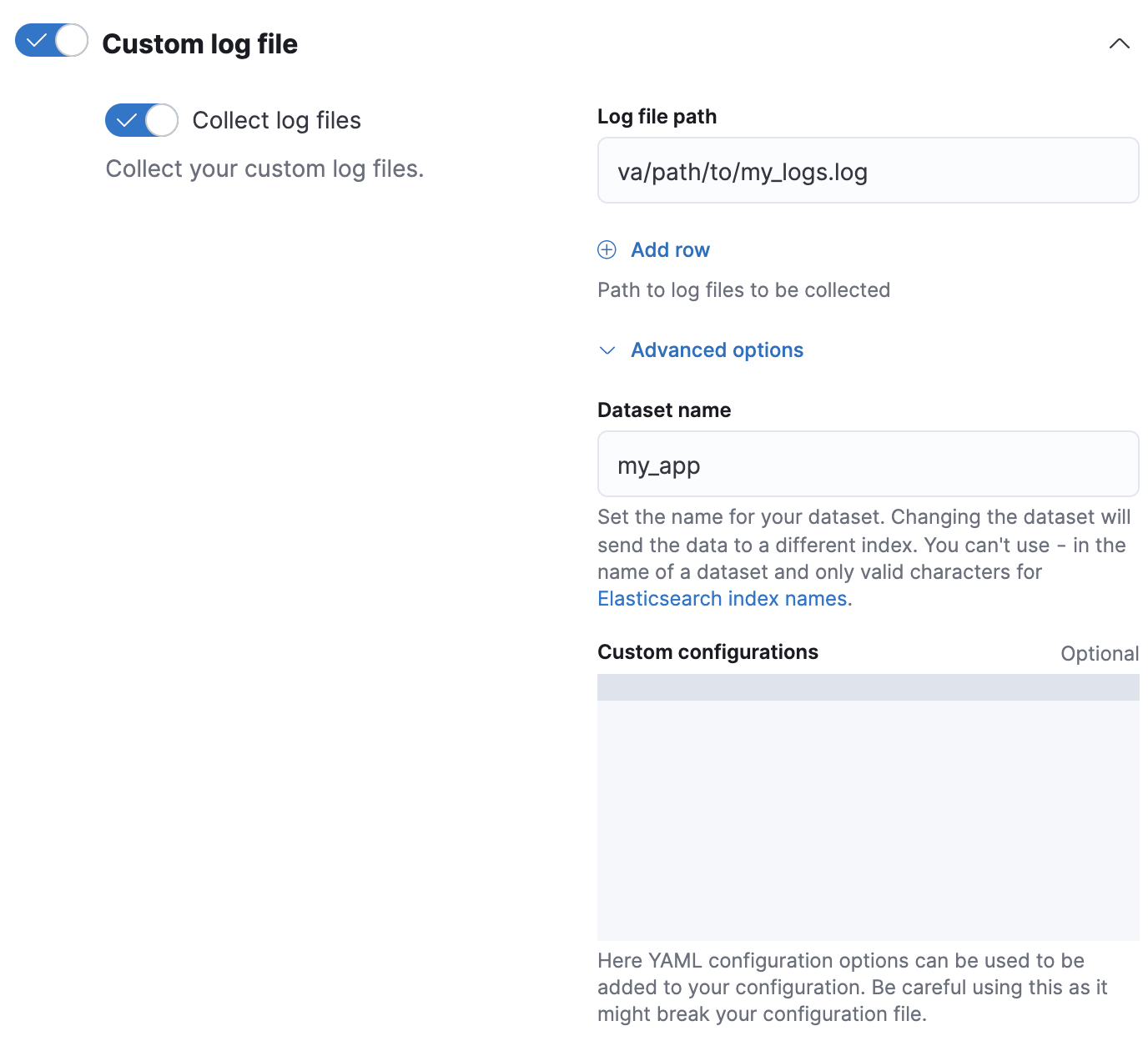
-
使用翻转 API来翻转您的数据流。这确保了 Elasticsearch 将索引模板及其管道设置应用于该集成的任何新数据。
resp = client.indices.rollover( alias="logs-my_app-default", ) print(resp)
response = client.indices.rollover( alias: 'logs-my_app-default' ) puts response
const response = await client.indices.rollover({ alias: "logs-my_app-default", }); console.log(response);
POST logs-my_app-default/_rollover/
-
创建并测试您的数据摄取管道。将您的管道命名为
logs-<数据集名称>-default。这使得跟踪集成的管道更加容易。例如,以下请求为
my-app数据集创建一个管道。管道的名称为logs-my_app-default。PUT _ingest/pipeline/logs-my_app-default { "description": "Pipeline for `my_app` dataset", "processors": [ ... ] }
- 在 Fleet 中添加或编辑自定义日志集成时,单击配置集成 > 自定义日志文件 > 高级选项。
-
在数据集名称中,指定您数据集的名称。Fleet 将为该集成将新数据添加到生成的
logs-<数据集名称>-default数据流中。例如,如果您数据集的名称为
my_app,则 Fleet 会将新数据添加到logs-my_app-default数据流中。 -
在自定义配置中,在
pipeline策略设置中指定您的管道。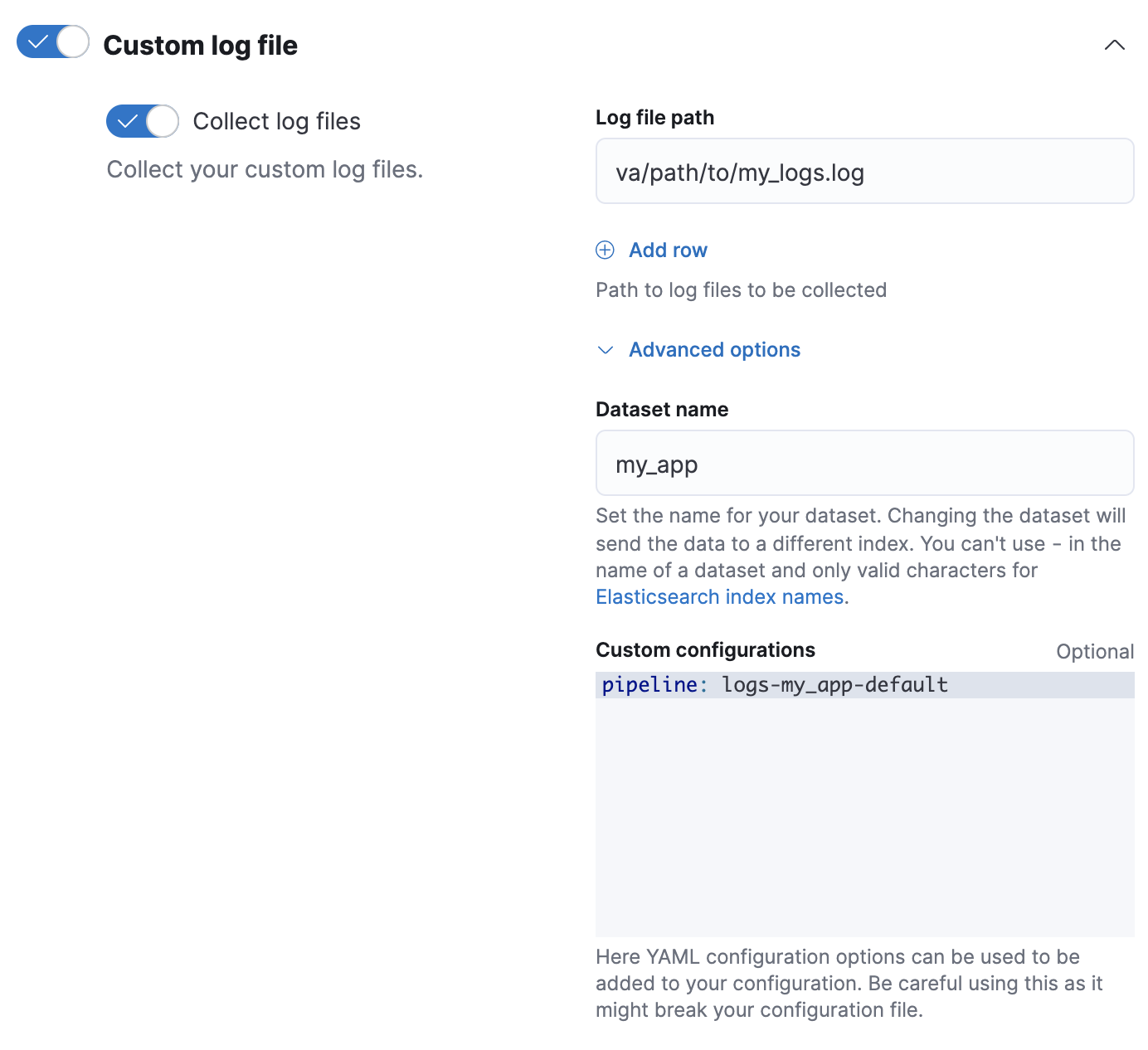
Elastic Agent 独立版
如果以独立模式运行 Elastic Agent,您可以使用包含 索引模板 来应用管道,该索引模板包含 index.default_pipeline 或 index.final_pipeline 索引设置。或者,您可以在 elastic-agent.yml 配置中指定 pipeline 策略设置。请参阅安装独立 Elastic Agent。
用于搜索索引的管道
编辑当您为搜索用例创建 Elasticsearch 索引时,例如使用 网络爬虫 或 连接器,这些索引会自动设置特定的摄取管道。这些处理器有助于优化您的搜索内容。有关更多信息,请参阅 搜索中的摄取管道。
在处理器中访问源字段
编辑处理器具有对传入文档的源字段的读写访问权限。要在处理器中访问字段键,请使用其字段名称。以下 set 处理器访问 my-long-field。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "field": "my-long-field", "value": 10 } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { field: 'my-long-field', value: 10 } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { field: "my-long-field", value: 10, }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "field": "my-long-field", "value": 10 } } ] }
您也可以添加 _source 前缀。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "field": "_source.my-long-field", "value": 10 } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { field: '_source.my-long-field', value: 10 } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { field: "_source.my-long-field", value: 10, }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "field": "_source.my-long-field", "value": 10 } } ] }
使用点表示法访问对象字段。
如果您的文档包含扁平化对象,请先使用 dot_expander 处理器来展开它们。其他摄取处理器无法访问扁平化对象。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "dot_expander": { "description": "Expand 'my-object-field.my-property'", "field": "my-object-field.my-property" } }, { "set": { "description": "Set 'my-object-field.my-property' to 10", "field": "my-object-field.my-property", "value": 10 } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { dot_expander: { description: "Expand 'my-object-field.my-property'", field: 'my-object-field.my-property' } }, { set: { description: "Set 'my-object-field.my-property' to 10", field: 'my-object-field.my-property', value: 10 } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { dot_expander: { description: "Expand 'my-object-field.my-property'", field: "my-object-field.my-property", }, }, { set: { description: "Set 'my-object-field.my-property' to 10", field: "my-object-field.my-property", value: 10, }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "dot_expander": { "description": "Expand 'my-object-field.my-property'", "field": "my-object-field.my-property" } }, { "set": { "description": "Set 'my-object-field.my-property' to 10", "field": "my-object-field.my-property", "value": 10 } } ] }
一些处理器参数支持 Mustache 模板片段。要在模板片段中访问字段值,请将字段名称括在三个大括号中:{{{field-name}}}。您可以使用模板片段来动态设置字段名称。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "description": "Set dynamic '<service>' field to 'code' value", "field": "{{{service}}}", "value": "{{{code}}}" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { description: "Set dynamic '<service>' field to 'code' value", field: '{{{service}}}', value: '{{{code}}}' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { description: "Set dynamic '<service>' field to 'code' value", field: "{{{service}}}", value: "{{{code}}}", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "description": "Set dynamic '<service>' field to 'code' value", "field": "{{{service}}}", "value": "{{{code}}}" } } ] }
在处理器中访问元数据字段
编辑处理器可以通过名称访问以下元数据字段
-
_index -
_id -
_routing -
_dynamic_templates
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "description": "Set '_routing' to 'geoip.country_iso_code' value", "field": "_routing", "value": "{{{geoip.country_iso_code}}}" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { description: "Set '_routing' to 'geoip.country_iso_code' value", field: '_routing', value: '{{{geoip.country_iso_code}}}' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { description: "Set '_routing' to 'geoip.country_iso_code' value", field: "_routing", value: "{{{geoip.country_iso_code}}}", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "description": "Set '_routing' to 'geoip.country_iso_code' value", "field": "_routing", "value": "{{{geoip.country_iso_code}}}" } } ] }
使用 Mustache 模板片段访问元数据字段值。例如,{{{_routing}}} 检索文档的路由值。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "description": "Use geo_point dynamic template for address field", "field": "_dynamic_templates", "value": { "address": "geo_point" } } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { description: 'Use geo_point dynamic template for address field', field: '_dynamic_templates', value: { address: 'geo_point' } } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { description: "Use geo_point dynamic template for address field", field: "_dynamic_templates", value: { address: "geo_point", }, }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "description": "Use geo_point dynamic template for address field", "field": "_dynamic_templates", "value": { "address": "geo_point" } } } ] }
如果索引的映射中尚未定义 address 字段,则上面的 set 处理器会告诉 ES 将名为 geo_point 的动态模板用于 address 字段。如果批量请求中已经定义了 address 字段的动态模板,则此处理器会覆盖该动态模板,但对批量请求中定义的其他动态模板没有影响。
如果您自动生成文档 ID,则不能在处理器中使用 {{{_id}}}。Elasticsearch 会在摄取后分配自动生成的 _id 值。
在处理器中访问摄取元数据
编辑摄取处理器可以使用 _ingest 键添加和访问摄取元数据。
与源字段和元数据字段不同,Elasticsearch 默认情况下不会为摄取元数据字段建立索引。Elasticsearch 还允许以 _ingest 键开头的源字段。如果您的数据包含此类源字段,请使用 _source._ingest 访问它们。
管道默认情况下仅创建 _ingest.timestamp 摄取元数据字段。此字段包含 Elasticsearch 收到文档索引请求时的时间戳。要为 _ingest.timestamp 或其他摄取元数据字段建立索引,请使用 set 处理器。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "description": "Index the ingest timestamp as 'event.ingested'", "field": "event.ingested", "value": "{{{_ingest.timestamp}}}" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { description: "Index the ingest timestamp as 'event.ingested'", field: 'event.ingested', value: '{{{_ingest.timestamp}}}' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { description: "Index the ingest timestamp as 'event.ingested'", field: "event.ingested", value: "{{{_ingest.timestamp}}}", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "description": "Index the ingest timestamp as 'event.ingested'", "field": "event.ingested", "value": "{{{_ingest.timestamp}}}" } } ] }
处理管道故障
编辑管道的处理器按顺序运行。默认情况下,当其中一个处理器失败或遇到错误时,管道处理会停止。
要忽略处理器故障并运行管道的其余处理器,请将 ignore_failure 设置为 true。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "rename": { "description": "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", "field": "provider", "target_field": "cloud.provider", "ignore_failure": True } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { rename: { description: "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", field: 'provider', target_field: 'cloud.provider', ignore_failure: true } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { rename: { description: "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", field: "provider", target_field: "cloud.provider", ignore_failure: true, }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "rename": { "description": "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", "field": "provider", "target_field": "cloud.provider", "ignore_failure": true } } ] }
使用 on_failure 参数指定在处理器失败后立即运行的处理器列表。如果指定了 on_failure,即使 on_failure 配置为空,Elasticsearch 之后也会运行管道的其余处理器。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "rename": { "description": "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", "field": "provider", "target_field": "cloud.provider", "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Set 'error.message'", "field": "error.message", "value": "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", "override": False } } ] } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { rename: { description: "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", field: 'provider', target_field: 'cloud.provider', on_failure: [ { set: { description: "Set 'error.message'", field: 'error.message', value: "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", override: false } } ] } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { rename: { description: "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", field: "provider", target_field: "cloud.provider", on_failure: [ { set: { description: "Set 'error.message'", field: "error.message", value: "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", override: false, }, }, ], }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "rename": { "description": "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", "field": "provider", "target_field": "cloud.provider", "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Set 'error.message'", "field": "error.message", "value": "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", "override": false } } ] } } ] }
嵌套 on_failure 处理器的列表以进行嵌套的错误处理。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "rename": { "description": "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", "field": "provider", "target_field": "cloud.provider", "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Set 'error.message'", "field": "error.message", "value": "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", "override": False, "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Set 'error.message.multi'", "field": "error.message.multi", "value": "Document encountered multiple ingest errors", "override": True } } ] } } ] } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { rename: { description: "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", field: 'provider', target_field: 'cloud.provider', on_failure: [ { set: { description: "Set 'error.message'", field: 'error.message', value: "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", override: false, on_failure: [ { set: { description: "Set 'error.message.multi'", field: 'error.message.multi', value: 'Document encountered multiple ingest errors', override: true } } ] } } ] } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { rename: { description: "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", field: "provider", target_field: "cloud.provider", on_failure: [ { set: { description: "Set 'error.message'", field: "error.message", value: "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", override: false, on_failure: [ { set: { description: "Set 'error.message.multi'", field: "error.message.multi", value: "Document encountered multiple ingest errors", override: true, }, }, ], }, }, ], }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "rename": { "description": "Rename 'provider' to 'cloud.provider'", "field": "provider", "target_field": "cloud.provider", "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Set 'error.message'", "field": "error.message", "value": "Field 'provider' does not exist. Cannot rename to 'cloud.provider'", "override": false, "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Set 'error.message.multi'", "field": "error.message.multi", "value": "Document encountered multiple ingest errors", "override": true } } ] } } ] } } ] }
您还可以为管道指定 on_failure。如果一个没有 on_failure 值的处理器失败,Elasticsearch 会使用此管道级别的参数作为回退。Elasticsearch 不会尝试运行管道的其余处理器。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ ... ], "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Index document to 'failed-<index>'", "field": "_index", "value": "failed-{{{ _index }}}" } } ] }
管道故障的其他信息可能在文档元数据字段 on_failure_message、on_failure_processor_type、on_failure_processor_tag 和 on_failure_pipeline 中可用。这些字段仅可从 on_failure 块内访问。
以下示例使用元数据字段在文档中包含有关管道故障的信息。
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ ... ], "on_failure": [ { "set": { "description": "Record error information", "field": "error_information", "value": "Processor {{ _ingest.on_failure_processor_type }} with tag {{ _ingest.on_failure_processor_tag }} in pipeline {{ _ingest.on_failure_pipeline }} failed with message {{ _ingest.on_failure_message }}" } } ] }
有条件地运行处理器
编辑每个处理器都支持可选的 if 条件,该条件编写为 Painless 脚本。如果提供,则仅当 if 条件为 true 时,处理器才会运行。
if 条件脚本在 Painless 的 摄取处理器上下文 中运行。在 if 条件中,ctx 值是只读的。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents with 'network.name' of 'Guest'", "if": "ctx?.network?.name == 'Guest'" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { drop: { description: "Drop documents with 'network.name' of 'Guest'", if: "ctx?.network?.name == 'Guest'" } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { drop: { description: "Drop documents with 'network.name' of 'Guest'", if: "ctx?.network?.name == 'Guest'", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents with 'network.name' of 'Guest'", "if": "ctx?.network?.name == 'Guest'" } } ] }
如果启用了 script.painless.regex.enabled 集群设置,则可以在 if 条件脚本中使用正则表达式。有关支持的语法,请参阅 Painless 正则表达式。
如果可能,请避免使用正则表达式。代价高昂的正则表达式会降低索引速度。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "set": { "description": "If 'url.scheme' is 'http', set 'url.insecure' to true", "if": "ctx.url?.scheme =~ /^http[^s]/", "field": "url.insecure", "value": True } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'my-pipeline', body: { processors: [ { set: { description: "If 'url.scheme' is 'http', set 'url.insecure' to true", if: 'ctx.url?.scheme =~ /^http[^s]/', field: 'url.insecure', value: true } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { set: { description: "If 'url.scheme' is 'http', set 'url.insecure' to true", if: "ctx.url?.scheme =~ /^http[^s]/", field: "url.insecure", value: true, }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "set": { "description": "If 'url.scheme' is 'http', set 'url.insecure' to true", "if": "ctx.url?.scheme =~ /^http[^s]/", "field": "url.insecure", "value": true } } ] }
您必须将 if 条件指定为单行上的有效 JSON。但是,您可以使用 Kibana 控制台的三引号语法来编写和调试更大的脚本。
如果可能,请避免使用复杂或代价高昂的 if 条件脚本。代价高昂的条件脚本会降低索引速度。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents that don't contain 'prod' tag", "if": "\n Collection tags = ctx.tags;\n if(tags != null){\n for (String tag : tags) {\n if (tag.toLowerCase().contains('prod')) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n }\n return true;\n " } } ], ) print(resp)
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { drop: { description: "Drop documents that don't contain 'prod' tag", if: "\n Collection tags = ctx.tags;\n if(tags != null){\n for (String tag : tags) {\n if (tag.toLowerCase().contains('prod')) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n }\n return true;\n ", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents that don't contain 'prod' tag", "if": """ Collection tags = ctx.tags; if(tags != null){ for (String tag : tags) { if (tag.toLowerCase().contains('prod')) { return false; } } } return true; """ } } ] }
您还可以指定一个 存储的脚本作为 if 条件。
resp = client.put_script( id="my-prod-tag-script", script={ "lang": "painless", "source": "\n Collection tags = ctx.tags;\n if(tags != null){\n for (String tag : tags) {\n if (tag.toLowerCase().contains('prod')) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n }\n return true;\n " }, ) print(resp) resp1 = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents that don't contain 'prod' tag", "if": { "id": "my-prod-tag-script" } } } ], ) print(resp1)
const response = await client.putScript({ id: "my-prod-tag-script", script: { lang: "painless", source: "\n Collection tags = ctx.tags;\n if(tags != null){\n for (String tag : tags) {\n if (tag.toLowerCase().contains('prod')) {\n return false;\n }\n }\n }\n return true;\n ", }, }); console.log(response); const response1 = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { drop: { description: "Drop documents that don't contain 'prod' tag", if: { id: "my-prod-tag-script", }, }, }, ], }); console.log(response1);
PUT _scripts/my-prod-tag-script { "script": { "lang": "painless", "source": """ Collection tags = ctx.tags; if(tags != null){ for (String tag : tags) { if (tag.toLowerCase().contains('prod')) { return false; } } } return true; """ } } PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents that don't contain 'prod' tag", "if": { "id": "my-prod-tag-script" } } } ] }
传入的文档通常包含对象字段。如果处理器脚本尝试访问其父对象不存在的字段,则 Elasticsearch 会返回 NullPointerException。为避免这些异常,请使用 空安全运算符,例如 ?.,并编写您的脚本以保证空安全。
例如,ctx.network?.name.equalsIgnoreCase('Guest') 不是空安全的。ctx.network?.name 可以返回 null。将脚本重写为 'Guest'.equalsIgnoreCase(ctx.network?.name),这是空安全的,因为 Guest 始终是非 null 的。
如果您无法重写脚本以保证空安全,请包含一个显式的 null 检查。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="my-pipeline", processors=[ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents that contain 'network.name' of 'Guest'", "if": "ctx.network?.name != null && ctx.network.name.contains('Guest')" } } ], ) print(resp)
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "my-pipeline", processors: [ { drop: { description: "Drop documents that contain 'network.name' of 'Guest'", if: "ctx.network?.name != null && ctx.network.name.contains('Guest')", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/my-pipeline { "processors": [ { "drop": { "description": "Drop documents that contain 'network.name' of 'Guest'", "if": "ctx.network?.name != null && ctx.network.name.contains('Guest')" } } ] }
有条件地应用管道
编辑将 if 条件与 pipeline 处理器结合使用,以根据您的条件将其他管道应用于文档。您可以使用此管道作为 默认管道,在用于配置多个数据流或索引的索引模板中。
resp = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id="one-pipeline-to-rule-them-all", processors=[ { "pipeline": { "description": "If 'service.name' is 'apache_httpd', use 'httpd_pipeline'", "if": "ctx.service?.name == 'apache_httpd'", "name": "httpd_pipeline" } }, { "pipeline": { "description": "If 'service.name' is 'syslog', use 'syslog_pipeline'", "if": "ctx.service?.name == 'syslog'", "name": "syslog_pipeline" } }, { "fail": { "description": "If 'service.name' is not 'apache_httpd' or 'syslog', return a failure message", "if": "ctx.service?.name != 'apache_httpd' && ctx.service?.name != 'syslog'", "message": "This pipeline requires service.name to be either `syslog` or `apache_httpd`" } } ], ) print(resp)
response = client.ingest.put_pipeline( id: 'one-pipeline-to-rule-them-all', body: { processors: [ { pipeline: { description: "If 'service.name' is 'apache_httpd', use 'httpd_pipeline'", if: "ctx.service?.name == 'apache_httpd'", name: 'httpd_pipeline' } }, { pipeline: { description: "If 'service.name' is 'syslog', use 'syslog_pipeline'", if: "ctx.service?.name == 'syslog'", name: 'syslog_pipeline' } }, { fail: { description: "If 'service.name' is not 'apache_httpd' or 'syslog', return a failure message", if: "ctx.service?.name != 'apache_httpd' && ctx.service?.name != 'syslog'", message: 'This pipeline requires service.name to be either `syslog` or `apache_httpd`' } } ] } ) puts response
const response = await client.ingest.putPipeline({ id: "one-pipeline-to-rule-them-all", processors: [ { pipeline: { description: "If 'service.name' is 'apache_httpd', use 'httpd_pipeline'", if: "ctx.service?.name == 'apache_httpd'", name: "httpd_pipeline", }, }, { pipeline: { description: "If 'service.name' is 'syslog', use 'syslog_pipeline'", if: "ctx.service?.name == 'syslog'", name: "syslog_pipeline", }, }, { fail: { description: "If 'service.name' is not 'apache_httpd' or 'syslog', return a failure message", if: "ctx.service?.name != 'apache_httpd' && ctx.service?.name != 'syslog'", message: "This pipeline requires service.name to be either `syslog` or `apache_httpd`", }, }, ], }); console.log(response);
PUT _ingest/pipeline/one-pipeline-to-rule-them-all { "processors": [ { "pipeline": { "description": "If 'service.name' is 'apache_httpd', use 'httpd_pipeline'", "if": "ctx.service?.name == 'apache_httpd'", "name": "httpd_pipeline" } }, { "pipeline": { "description": "If 'service.name' is 'syslog', use 'syslog_pipeline'", "if": "ctx.service?.name == 'syslog'", "name": "syslog_pipeline" } }, { "fail": { "description": "If 'service.name' is not 'apache_httpd' or 'syslog', return a failure message", "if": "ctx.service?.name != 'apache_httpd' && ctx.service?.name != 'syslog'", "message": "This pipeline requires service.name to be either `syslog` or `apache_httpd`" } } ] }
获取管道使用情况统计信息
编辑使用 节点统计 API 获取全局和每个管道的摄取统计信息。使用这些统计信息来确定哪些管道运行最频繁或花费最多的处理时间。
resp = client.nodes.stats( metric="ingest", filter_path="nodes.*.ingest", ) print(resp)
response = client.nodes.stats( metric: 'ingest', filter_path: 'nodes.*.ingest' ) puts response
const response = await client.nodes.stats({ metric: "ingest", filter_path: "nodes.*.ingest", }); console.log(response);
GET _nodes/stats/ingest?filter_path=nodes.*.ingest
On this page